The Task Manager has been around for a long time.
The app gives you access to many functions that can help with your efforts to monitor, control and optimise your operating system. It can also be used to diagnose system problems by showing abnormal use of resources. High usage of CPU, Memory, network or disk usage can indicate problems whose cause needs to be found and reduced. If you are tweaking your system settings you will want to see how effective they are by reviewing the relevant categories.
The Task Manager has been around for a long time.
The app gives you access to many functions that can help with your efforts to monitor, control and optimise your operating system. It can also be used to diagnose system problems by showing abnormal use of resources. High usage of CPU, Memory, network or disk usage can indicate problems whose cause needs to be found and reduced. If you are tweaking your system settings you will want to see how effective they are by reviewing the relevant categories.
Cool Geek Clues
PC Performance Using the Task Manager
The performance tab shows information that allows the user to assess various parameters in a graphical and data format. This can indicate if the system is performing as expected or additional investigation is required.
The available categories depend on your system configuration
Some functionality is duplicated in the companion tool Resource Monitor.
When you enter the performance tab after opening the task manager the default view is the CPU category.
CPU
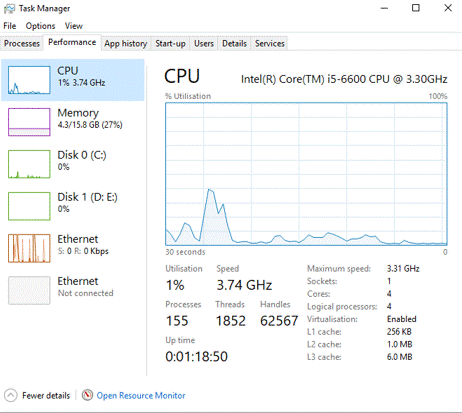
Default View
-
The CPU Category provides a real time graphic which will provide a visual if there is excessive CPU usage. With current hardware CPU RAM memory is sufficient for low usage -high usage needs to investigate ans cause allocated.
-
Under the graphic are real time data values which can also be investigated for any expected anomalies.
-
First row shows Utilisation, Speed available the CPU, and details of the CPU ores
-
Next row shows :
-
Processes - support for a specific software/hardware
-
Threads - A thread is part of a process. Each process can have more than one thread within it that can executed in parallel.
-
Handles are separate files that can be accessed by threads. A thread can access many handles.
-


Compact View - Double click the relevant icon in left panel. If you double click any icon in the compact view it will open to the full view again
Chart View - Double click on any chart and it will open to show chart only -works for charts in all categories
Memory

Selecting Memory shows two charts with details below then. The top chart shows memory usage, It has no scale values so you can only estimate the amount of memory in use. The lower chart shows how the memory has been allocated, If you hover over parts of this charts pop outs show more detail. The sections are :-
Standby - Memory that contains cached data and code that is not actively being used by the system
Free - Memory that is not currently in use and will be re-purposed first when processes,drivers and operating system need more memory
- In Use - Shows the amount of memory used for processes, drivers and the operating system. There is a sub section showing the amount of memory that is compressed by allocating it to the pagefile. If there is sufficient RAM very little or no compression takes place.
- Modified - Memory content that has to be saved to disk before use


- In Use - RAM currently in use
- Available - Memory that is available for use by the operating system
- Committed - Shows two values both relating to the virtual memory allocation contained in the pagefile file, The first is in the amount of memory the system allows for the pagefile (usually set to automatic but can be entered manually). The second value is the maximum amount of memory the virtual memory can use if the original size is used up.
- Cached- Is additional memory that is available from the modified and standby allocation.
- Paged Pool - Amount of system processes memory (kernel) in use that can be transferred to the pagefile should the RAM become full.
- Non-paged pool - Amount in the kernel that must be kept in the physical memory and cannot be transferred to the page file.
- Speed - RAM speed, not to be confused with CPU speed.
- Slots used - Number of available slots used for RAM modules
- Form Factor -Is the standard used to describe the physical aspects and pin configuration for the memory module. The most common is DIMM - Dual Inline Memory Module
- Hardware Reserved - The amount of RAM reserved for connected hardware devices
Disk

Disks are a critical component of the operating system. Persistent high active use of either reading or writing as shown above can be a sign of problems which will cause the system to become slow and unresponsive and the cause needs to be established and eliminated or reduced. Typical disk usage after boot up is low and has occasional peaks as Apps and files are read or written to the disk. The specif processes/services causing high usage can be viewed in the disk column in the Processes tab.
-
Active Time - How much time in percent is being spent reading/writing to the disk. The top chart maps this and the actual real time value is shown below.
-
Average Response Time - The number of data transfers per second to or from the disk. Usually measured in ms
-
Read Speed - Measured in KB/s. This is shown as the solid line in the lower Disk transfer rate chart. Consistent high transfer rates go together with high active time.
-
Write speed - Measured in KB/s. This is shown as the dashed line in the Disk transfer rate chart.
-
Capacity - Disk Capacity
-
Formatted - Amount of the disk that has been formatted, The disk may be segmented into different partitions which could contain a different operating system.
-
System disk - Does the disk under review contain the operating system files
-
Page File - Does the disk contain a page file also known as a swap file. It is used as additional storage if the RAM memory is struggling.
Ethernet

The network adapter name is on top of the chart.
The dotted line on the graph represents the Send rate and the solid line represents the received rate.
Right clicking on the chart opens a visual dynamic listing of may other parameters to give advanced diagnostic capabilities. This is shown below in the Wi-Fi section.
The information below the chart :
-
Send - The rate at which data is being sent through the network adaptor measured in kilo, mega or giga bits per second (Kbps, Mbps, Gbps)
-
Receive - The rate at which data is being received through the network adapter measured in kilo, mega or giga bits per second (Kbps, Mbps, Gbps)
-
Adapter Name - The adapter name can be change here - Control Panel\Network and Internet\Network Connections else a default system name will be given
-
DNS name - Domain Name System is a system of converting and alias name into a numeric IP address. The name is the server name that the network is connected to
-
Connection type - Ethernet
-
IPv4 address - Internet Protocol version 4 address is a 32 bit network reference. Usually broken down into 4 octets in decimal format has shown above.
-
IPv6 address - Internet Protocol version 6 address is a 128 bit network reference. The address is broken into 8 blocks each of which consts of 16 bits in hexadecimal format
Wi-Fi

The network adapter name is on top of the chart.
The dotted line on the graph represents the Send rate and the solid line represents the received rate.
Right clicking on the chart opens a visual dynamic listing of may other parameters to give advanced diagnostic capabilities. This is shown below.
The information below the chart :
-
Send - The rate at which data is being sent through the network adaptor measured in kilo, mega or giga bits per second (Kbps, Mbps, Gbps)
-
Receive - The rate at which data is being received through the network adapter measured in kilo, mega or giga bits per second (Kbps, Mbps, Gbps)
-
Adapter Name - The adapter name can be change here - Control Panel\Network and Internet\Network Connections else a default system name will be given
-
SSID - Service Set Identifier - The unique name given to a Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN). Can be changed in the network router settings via your browser.
-
DNS name - Domain Name System is a system of converting and alias name into a numeric IP address. The name is the server name that the network is connected to
-
Connection type - Is the WI-Fi standard in use. The standard for for most PC's and Lap Tops is 802.11. This can have suffixes of a,b,g,n and ac with each having different properties.
-
IPv4 address - Internet Protocol version 4 address is a 32 bit network reference. Usually broken down into 4 octets in decimal format has shown above.
-
IPv6 address - Internet Protocol version 6 address is a 128 bit network reference. The address is broken into 8 blocks each of which consts of 16 bits in hexadecimal format


